Cho hình bình hành ABCD có \(\widehat{BAD}=60^o\), AB =2a. Gọi E, F là trung điểm của BC , C. G là trọng tâm của tam gaics ACD.
Tính \(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+2\overrightarrow{AD}\right|\) theo a.
Cho hình bình hành ABCD. Gọi E là điểm thỏa mãn 4 \(\overrightarrow{DE}\) = \(\overrightarrow{DC}\) và G là trọng tâm tam giác ABE. Đường thẳng AG cắt BC tại F. Biểu diễn \(\overrightarrow{AG}\) theo \(\overrightarrow{AB}\) , \(\overrightarrow{AD}\) và tính tỉ số \(\dfrac{BF}{BC}\)
Cho ABCD là hình bình hành. Đặt \(\overrightarrow {AB} = \overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow {AD} = \overrightarrow b .\) Gọi G là trọng tâm của tam giác ABC. Biểu thị các vecto \(\overrightarrow {AG} ,\overrightarrow {CG} \) theo hai vecto \(\overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow b .\)
Cách 1:
Gọi O là giao điểm của AC và BD.

Ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AG} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow {BG} ;\\\overrightarrow {CG} = \overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow {DA} + \overrightarrow {BG} = - \overrightarrow b + \overrightarrow {BG} ;\end{array}\)(*)
Lại có: \(\overrightarrow {BD} =\overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {AD} = - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b \).
\(\overrightarrow {BG} ,\overrightarrow {BD} \) cùng phương và \(\left| {\overrightarrow {BG} } \right| = \frac{2}{3}BO = \frac{1}{3}\left| {\overrightarrow {BD} } \right|\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {BG} = \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {BD} = \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right)\)
Do đó (*) \( \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AG} = \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\\\overrightarrow {CG} = -\overrightarrow b + \overrightarrow {BG} = -\overrightarrow b + \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\;\overrightarrow {CG} = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b .\)
Cách 2:
Gọi AE, CF là các trung tuyến trong tam giác ABC.
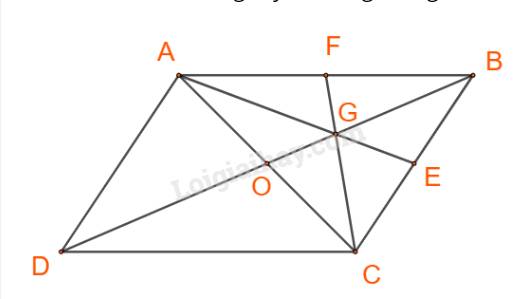
Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {AE} = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} } \right) = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left[ {\overrightarrow {AB} + \left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} } \right)} \right] \\= \frac{1}{3}\left( {2\overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b \)
\(\overrightarrow {CG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {CF} = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {CA} + \overrightarrow {CB} } \right) = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left[ {\left( {\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right) + \overrightarrow {CB} } \right] = \frac{1}{3}\left( {2\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right) = \frac{1}{3}\left( { - 2\overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} } \right) = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b \)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\;\overrightarrow {CG} = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b .\)
Cho hình bình hành ABCD có AB = 4, AD = 6, \(\widehat {BAD} = {60^o}\) (Hình 73).
a) Biểu thị các vecto \(\overrightarrow {BD} ,\overrightarrow {AC} \) theo \(\overrightarrow {AB} ,\overrightarrow {AD} .\)
b) Tính các tích vô hướng \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AD} ,\;\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} ,\;\overrightarrow {BD} .\overrightarrow {AC} .\)
c) Tính độ dài các đường chéo \(BD,AC.\)
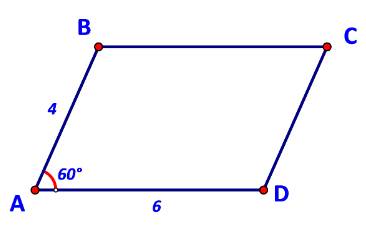
a) \(\overrightarrow {BD} = \overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} ;\;\overrightarrow {AC} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} .\)
b) \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AD} = 4.6.\cos \widehat {BAD} = 24.\cos {60^o} = 12.\)
\(\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = \overrightarrow {AB} (\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} ) = {\overrightarrow {AB} ^2} + \overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AD} = {4^2} + 12 = 28.\\\overrightarrow {BD} .\overrightarrow {AC} = (\overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} )(\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} ) = {\overrightarrow {AD} ^2} - {\overrightarrow {AB} ^2} = {6^2} - {4^2} = 20.\end{array}\)
c) Áp dụng định lí cosin cho tam giác ABD ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\quad \;B{D^2} = A{B^2} + A{D^2} - 2.AB.AD.\cos A\\ \Leftrightarrow B{D^2} = {4^2} + {6^2} - 2.4.6.\cos {60^o} = 28\\ \Leftrightarrow BD = 2\sqrt 7 .\end{array}\)
Áp dụng định lí cosin cho tam giác ABC ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\quad \;A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} - 2.AB.BC.\cos B\\ \Leftrightarrow A{C^2} = {4^2} + {6^2} - 2.4.6.\cos {120^o} = 76\\ \Leftrightarrow AC = 2\sqrt {19} .\end{array}\)
Cho tam giác ABC có \(AB = 2,AC = 3,\widehat {BAC} = {60^o}.\) Gọi M là trung điểm của đoạn thẳng BC. Điểm D thỏa mãn \(\overrightarrow {AD} = \frac{7}{{12}}\overrightarrow {AC} .\)
a) Tính \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} \)
b) Biểu diễn \(\overrightarrow {AM} ,\overrightarrow {BD} \) theo \(\overrightarrow {AB} ,\overrightarrow {AC} \)
c) Chứng minh \(AM \bot BD\).
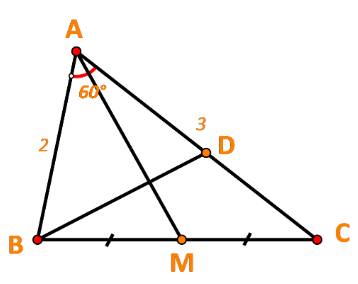
a) \(\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = 2.3.\cos \widehat {BAC} = 6.\cos {60^o} = 3\)
b)
Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} = 2\overrightarrow {AM} \)(do M là trung điểm của BC)
\( \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {AM} = \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AC} \)
+) \(\overrightarrow {BD} = \overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} = \frac{7}{{12}}\overrightarrow {AC} - \overrightarrow {AB} \)
c) Ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AM} .\overrightarrow {BD} = \left( {\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AC} } \right)\left( {\frac{7}{{12}}\overrightarrow {AC} - \overrightarrow {AB} } \right)\\ = \frac{7}{{24}}\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} - \frac{1}{2}{\overrightarrow {AB} ^2} + \frac{7}{{24}}{\overrightarrow {AC} ^2} - \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AC} .\overrightarrow {AB} \\ = - \frac{1}{2}A{B^2} + \frac{7}{{24}}A{C^2} - \frac{5}{{24}}\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} \\ = - \frac{1}{2}{.2^2} + \frac{7}{{24}}{.3^2} - \frac{5}{{24}}.3\\ = 0\end{array}\)
\( \Rightarrow AM \bot BD\)
Cho hình bình hành ABCD. Gọi M là trung điểm của cạnh BC. Hãy biểu thị \(\overrightarrow {AM} \) theo hai vecto \(\overrightarrow {AB} \) và \(\overrightarrow {AD} \).
Từ M kẻ đường thẳng song song với AB, cắt AD tại E.
Khi đó tứ giác ABME là hình bình hành.
Do đó: \(\overrightarrow {AM} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AE} \).
Dễ thấy: \(AE = BM = \frac{1}{2}BC = \frac{1}{2}AD\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {AE} = \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AD} \)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {AM} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AD} \)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {AM} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AD} \)
Chú ý khi giải
+) Dựng hình hình hành sao cho đường chéo là vecto cần biểu thị, 2 cạnh của nó song song với giá của hai vecto đang biểu thị theo.
Cho tam giác đều ABC, AB = 2a. Gọi M là trung điểm của cạnh BC.
a, Chứng minh rằng: \(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MA}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
b, Tính \(\left|\overrightarrow{AM}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right|\) theo a?
c, Tìm vị trí điểm N thỏa mãn: \(3\overrightarrow{NA}+3\overrightarrow{NB}+2\overrightarrow{NC}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
Có vẻ không đúng.
Giả sử \(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MA}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}+\left(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{AB}\right)=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MB}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\overrightarrow{MB}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M\equiv B\) (Vô lí)
Hình vẽ:
a, Chứng minh \(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BM}+\overrightarrow{MA}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
Ta có \(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BM}+\overrightarrow{MA}=\overrightarrow{BM}+\left(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{AB}\right)=\overrightarrow{BM}+\overrightarrow{MB}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
b, Gọi H là trung điểm \(MC\)
Ta có \(AM=\sqrt{AC^2-MC^2}=\sqrt{4a^2-a^2}=a\sqrt{3}\)
\(AH=\sqrt{AM^2+MH^2}=\sqrt{\left(a\sqrt{3}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{a}{2}\right)^2}=a.\dfrac{\sqrt{13}}{2}\)
\(\left|\overrightarrow{AM}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right|=\left|2\overrightarrow{AH}\right|=2AH=a\sqrt{13}\)
c, Gọi D là trung điểm AB
\(3\overrightarrow{NA}+3\overrightarrow{NB}+2\overrightarrow{NC}=3\left(\overrightarrow{NA}+\overrightarrow{NB}\right)+2\overrightarrow{NC}=6\overrightarrow{ND}+2\overrightarrow{NC}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{NC}=3\overrightarrow{DN}\)
Vậy N thuộc đoạn CD sao cho \(CN=\dfrac{3}{4}CD\)
Cho tam giác ABC có trọng tâm G, gọi I là trung điểm BC. Tìm tập hợp điểm M thỏa mãn: \(2\left|\overrightarrow{MC}+\overrightarrow{IA}-\overrightarrow{IM}-\overrightarrow{BM}\right|=3\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{MC}-\overrightarrow{AM}\right|\)
Gt ⇒ \(2\left|\overrightarrow{MC}+\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{MB}\right|=3\left|\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MC}\right|\)
Do G là trọng tâm của ΔABC
⇒ \(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MC}=3\overrightarrow{MG}\)
⇒ VT = 6MG
I là trung điểm của BC
⇒ \(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{MB}=2\overrightarrow{MI}\)
⇒ VP = 6MI
Khi VT = VP thì MG = MI
Vậy tập hợp các điểm M thỏa mãn ycbt là đường trung trực của đoạn thẳng IG
Cho hình thoi ABCD cạnh a, \(\widehat{BCD}\)= 60o . O là giao điểm của AC và BD . Tính \(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}\right|,\left|\overrightarrow{CB}+\overrightarrow{DC}\right|\)
Cho hình thoi ABCD có \(\widehat{BAD}\) = 60o và cạnh là a. Gọi O là giao điểm 2 đường chéo. Tính:
a) \(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}\right|\)
b) \(\left|\overrightarrow{BA}-\overrightarrow{BC}\right|\)
\(\widehat{BAD}=60^0\Rightarrow BD=a\) ; \(AC=2OA=2.\frac{a\sqrt{3}}{2}=a\sqrt{3}\)
\(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BC}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{AC}\right|=a\sqrt{3}\)
\(\left|\overrightarrow{BA}-\overrightarrow{BC}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{BA}+\overrightarrow{CB}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{CA}\right|=a\sqrt{3}\)