1) (x2 -2x +2 ) (x2 -2x +5 ) =40
x4 +x3 -10x2 +x +1 =0
Tìm a và b để đa thức A chia hết cho đa thức B với:
a) A = x 3 - 9 x 2 +17x - 25 + a và B = x 2 - 2x + 3;
b) A = x 4 - 7 x 3 + 10 x 2 +(a - 1)x + b - a và B = x 2 -6x + 5.
1. Tìm \(m\in\left[-10;10\right]\) để pt \(\left(x^2-2x+m\right)^2-2x^2+3x-m=0\) có 4 ng pb
2. Cho biết x1,x2 là nghiệm của pt \(x^2-x+a=0\) và x3,x4 là nghiệm của pt \(x^2-4x+b=0\) . Biết rằng \(\dfrac{x2}{x1}=\dfrac{x3}{x2}=\dfrac{x4}{x3}\), b >0 . Tìm a
1.
Đặt \(x^2-2x+m=t\), phương trình trở thành \(t^2-2t+m=x\)
Ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x+m=t\\t^2-2t+m=x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-t\right)\left(x+t-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=t\\x=1-t\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=x^2-2x+m\\x=1-x^2+2x-m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-x^2+3x\\m=-x^2+x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của \(y=-x^2+x+1\) và \(y=-x^2+3x\):
\(-x^2+x+1=-x^2+3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Đồ thị hàm số \(y=-x^2+3x\) và \(y=-x^2+x+1\):
Dựa vào đồ thị, yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi \(m< \dfrac{5}{4}\)
Mà \(m\in\left[-10;10\right]\Rightarrow m\in[-10;\dfrac{5}{4})\)
Bài 1: Giải các phương trình dưới đây
1) x2 - 9 = (x - 3)(5x +2)
2) x3 - 1 = (x - 1)(x2 - 2x +16)
3) 4x2 (x - 1) - x + 1 = 0
4) x3 + 4x2 - 9x - 36 = 0
5) (3x + 5)2 = (x - 1)2
6) 9 (2x + 1)2 = 4 (x - 5)2
7) x2 + 2x = 15
8) x4 + 5x3 + 4x2 = 0
9) (x2 - 4) - (x - 2)(3 - 2x) = 0
10) (3x + 2)(x2 - 1) = (9x2 - 4) (x + 1)
11) (3x - 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x - 1)(7x - 10)
12) (2x2 + 1) (4x - 3) = (x - 12)(2x2 + 1)
1: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(-4x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1-x^2+2x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-15\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;5\right\}\)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+4\right)-9\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=x-1\\3x+5=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-6\\4x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3-2x+10\right)\left(6x+3+2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+13\right)\left(8x-7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{13}{4};\dfrac{7}{8}\right\}\)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=5x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2-2x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
3.
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
7.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
8.\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3+4x^3+4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+1\right)+4x^2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+4x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=0;x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bài 2: Tính
a) ( x4 - x3 + x2 + 3x ) : ( x2 - 2x + 3 )
b) ( 21x2y3 ) : ( 6xy)
c) x2- 36 : ( 2x + 10) ( 6 - x )
d) 2x2 ( 3x - 5 )
e) ( 12x3y + 18x2y) : 2xy
g) ( x2 + 2x + 1 ) : ( x + 1 )
h) 5y ( 2y - 1 ) - ( 3y + 2 ) ( 3 - 3y)
i) ( 6x3 - x2 + 5x - 1 ) : ( 2x - 1 )
`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`

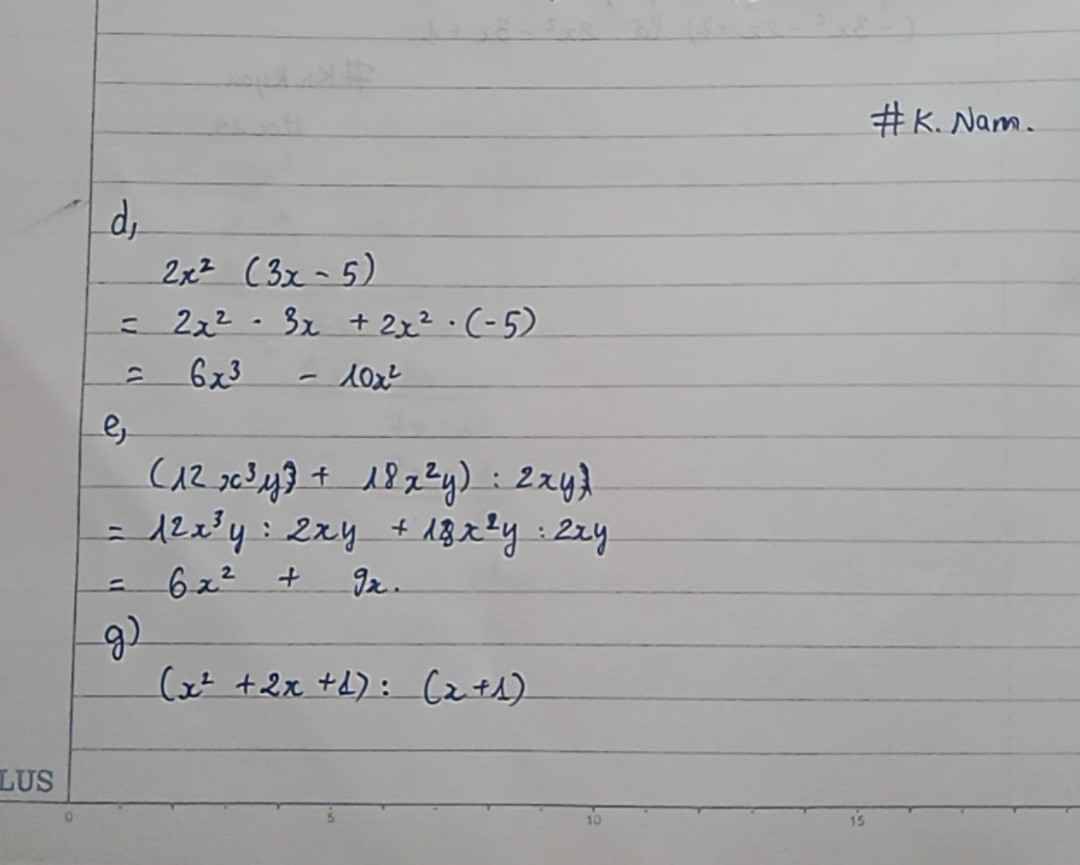

*Máy tớ cam hơi mờ, cậu thông cảm ._.*
Cậu viết lại rõ đề câu c, nhé.
Bài 1. Làm tính nhân:
a) 3x2 (2 - 5xy)
b) -\(\dfrac{2}{3}\) xy (xy2 - x3 + 4)
c) ( x - 7 y )( xy + 1)
Bài 2. Rút gọn các biểu thức sau:
a) 5x(4x2 - 2x +1) - 2x(10x2 - 5x - 2)
b) 3x( x - 2) - 5x(1- x) - 8(x2 - 3)
d) (x3 - 2x)(x2 +1)
Bài 1:
\(a,6x^2-15x^3y\\ b,=-\dfrac{2}{3}x^2y^3+\dfrac{2}{3}x^4y-\dfrac{8}{3}xy\)
Bài 2:
\(a,=20x^3-10x^2+5x-20x^3+10x^2+4x=9x\\ b,=3x^2-6x-5x+5x^2-8x^2+24=24-11x\\ c,=x^5+x^3-2x^3-2x=x^5-x^3-2x\)
câu d của bài 2 là của bài 1 nha mình để nhầm chỗ huhu
a) ( 6x3 - 7x2 - x + 2 ) : ( 2x + 1 )
b) ( x4 - x3 + x2 + 3x ) : ( x2 - 2x + 3 )
\(a,=\left(6x^3+3x^2-10x^2-5x+4x+2\right):\left(2x+1\right)\\ =\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x^2-5x+2\right):\left(2x+1\right)=3x^2-5x+2\\ b,=\left(x^4-2x^3+3x^2+x^3-2x^2+3x\right):\left(x^2-2x+3\right)\\ =\left(x^2-2x+3\right)\left(x^2+x\right):\left(x^2-2x+3\right)=x^2+x\)
a) 2x2(x-2)+3x(x2-x-2)-5(3-x2)
b) (x-1)(x-3)-(4-x)(2x+1)-3x2+2x-5
c) (x4-x3-3x2+x+2):(x2-1)
Mọi người giải giúp em với
phân tích thành nhân tử:
a, (ab-1)2 +( a+b)2 x3 + 2x2 + 2x + 1;
c, x3 - 4x2 + 12x - 27; x4 - 2x3 + 2x -1
d, x4 +2x3+ 2x2 +2x + 1 x2-2x-4y2-4y
e, x4 + 2x3 - 4x -4 x2(1 - x2) - 4 - 4x2
f, (1 + 2x) (1-2x) - x(x+2)(x-2) x2 + y2 - x2y2 + xy- x - y
1) x3-x2+2x-2 4) ax-2x-a2+2a 7) x2-6xy-25z2+9y2
2) x2-y2+2x+2y 5) 2xy +3z+6y+xz 8) x3-2x2+x
3) x2/4+2xy+4y2-25 6) x2y2+yz+y3+zx2 9) x4+4
Bài 1:phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử
a)x2-2x-4y2-4y e)x4+2x3+2x2+2x+1
b)x3+2x2+2x+1 f)x5+x4+x3+x2+x+1
c)x3-4x2+12x-27
d)a6-a4+2a3+2a2
Làm chi tiết giúp mình với ạ, cảm ơn
a) \(x^2-2x-4y^2-4y=\left(x^2-4y^2\right)-\left(2x+4y\right)=\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)-2\left(x+2y\right)=\left(x+2y\right)\left(x-2y-2\right)\)
b) \(x^3+2x^2+2x+1=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1+2x\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
c) \(x^3-4x^2+12x-27=x^3-3x^2-x^2+3x+9x-27=x^2\left(x-3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)+9\left(x-3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2-x+9\right)\)
d) \(a^6-a^4+2a^3+2a^2=a^2\left(a^4-a^2+2a+2\right)=a^2\left[a^2\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)+2\left(a+1\right)\right]=a^2\left(a+1\right)\left(a^3-a^2+2\right)=a^2\left(a+1\right)\left[a^3+a^2-2a^2+2\right]=a^2\left(a+1\right)\left[a^2\left(a+1\right)-2\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)\right]=a^2\left(a+1\right)^2\left(a^2-2a+2\right)\)
a) Ta có: \(x^2-2x-4y^2-4y\)
\(=\left(x^2-4y^2\right)-\left(2x+4y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)-2\left(x+2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+2y\right)\left(x-2y-2\right)\)
b) Ta có: \(x^3+2x^2+2x+1\)
\(=\left(x^3+1\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
d) Ta có: \(a^6-a^4+2a^3+2a^2\)
\(=a^2\left(a^4-a^2+2a+2\right)\)
\(=a^2\left[a^2\left(a^2-1\right)+\left(2a+2\right)\right]\)
\(=a^2\left[a^2\left(a-1\right)\left(a+1\right)+2\left(a+1\right)\right]\)
\(=a^2\cdot\left(a+1\right)\left(a^3-a+2\right)\)
c) Ta có: \(x^3-4x^2+12x-27\)
\(=\left(x^3-27\right)-\left(4x^2-12x\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)-4x\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2-x+9\right)\)