Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên:
x2 + x + y2= 2\(\sqrt{x-1}+2xy\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
a) Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình: \(2y^2-x+2xy=y+4\)
b) Giải phương trình : ( \(1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}\))(\(\sqrt{x^2+1}-x\)) = 1
\(\left(1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-x\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}}{\sqrt{x^2+1}+x}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}=\sqrt{x^2+1}+x\)
\(\Rightarrow1+x\sqrt{x^2+1}-\sqrt{x^2+1}-x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\\sqrt{x^2+1}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\\sqrt{x^2+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x^2+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
\(a,2y^2-x+2xy=y+4\\ \Leftrightarrow2y\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2y-1\right)\left(x+y\right)=4=4\cdot1=\left(-4\right)\left(-1\right)=\left(-2\right)\left(-2\right)=2\cdot2\)
Vì \(x,y\in Z\Leftrightarrow2y-1\) lẻ
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y-1=1\\x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y-1=-1\\x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left\{\left(3;1\right);\left(4;0\right)\right\}\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên : x2-x=y2-1
Bài 1:a) Chứng minh rằng không tồn tại các cặp số x,y thỏa mãn:
8x2+26xy+29y2=10001
b) Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên 2xy-2y+x^2-4x+2=0
c) Giải phương trình 4+2\(\sqrt{2-2x^2}\)=3\(\sqrt{x}+3\sqrt{2-x}\)
bài 1 phân tích các đa thức thành nhân tử a) x2 - z2 + y2 - 2xy b) a3 - ay - a2x + xy c) x2 - 2xy + y2 - xz + yz d) x2 - 2xy + tx - 2ty bài 2 giải các phương trình sau ( x - 2 )2 - ( x - 3 ) ( x+ 3 ) 6 bài 3 chứng minh rằng a) x2 + 2x + 2 0 với xϵZb) -x2 + 4x - 5 0 với x ϵ Z
Đọc tiếp
bài 1 phân tích các đa thức thành nhân tử
a) x2 - z2 + y2 - 2xy b) a3 - ay - a2x + xy
c) x2 - 2xy + y2 - xz + yz d) x2 - 2xy + tx - 2ty
bài 2 giải các phương trình sau
( x - 2 )2 - ( x - 3 ) ( x+ 3 ) = 6
bài 3 chứng minh rằng
a) x2 + 2x + 2 > 0 với xϵZ
b) -x2 + 4x - 5 < 0 với x ϵ Z
\(1,\\ a,=\left(x-y\right)^2-z^2=\left(x-y-z\right)\left(x-y+z\right)\\ b,=a^2\left(a-x\right)-y\left(a-x\right)=\left(a^2-y\right)\left(a-x\right)\\ c,=\left(x-y\right)^2-z\left(x-y\right)=\left(x-y\right)\left(x-y-z\right)\\ d,=x\left(x-2y\right)+t\left(x-2y\right)=\left(x+t\right)\left(x-2y\right)\\ 2,\\ \Rightarrow x^2-4x+4-x^2+9=6\\ \Rightarrow-4x=-7\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{4}\\ 3,\\ a,x^2+2x+2=\left(x+1\right)^2+1\ge1>0\\ b,-x^2+4x-5=-\left(x-2\right)^2-1\le-1< 0\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: 2x3+2x2y+x2+2xy=x+10
giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: x+y+xy=x2+y2
\(x+y+xy=x^2+y^2\)
⇔ \(2xy+2x+2y=2x^2+2y^2\)
⇔ \(\left(x^2+y^2-2xy\right)+\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)=2\)
⇔ \(\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2=2\)
⇔ 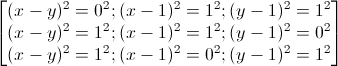
⇔ 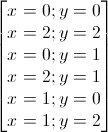
Các cặp số nguyên (x, y) thỏa mãn phương trình là : (0; 0); (2; 2); (0; 1); (2; 1); (1; 0);(1;2).
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
a) Tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình : \(xy^2+2xy-243y+x=0\)
b) Giải phương trình: \(\sqrt{x^2+12}+5=3x+\sqrt{x^2+5}\)
a) xy2 + 2xy - 243y + x = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x ( y + 1 )2 = 243y
Mà ( y ; y + 1 ) = 1 nên 243 \(⋮\)( y + 1 )2
Mặt khác ( y + 1 ) 2 là số chính phương nên ( y + 1 )2 \(\in\){ 32 ; 92 }
+) ( y + 1 )2 = 32 \(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y+1=3\\y+1=-3\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=2\Rightarrow x=54\\y=-4\Rightarrow x=-108\end{cases}}}\)
+) ( y + 1 )2 = 92 \(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y+1=9\\y+1=-9\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=8\Rightarrow x=24\\y=-10\Rightarrow x=-30\end{cases}}}\)
vậy ...
b) \(\sqrt{x^2+12}+5=3x+\sqrt{x^2+5}\)( đk : x > 0 )
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+12}-4=3x+\sqrt{x^2+5}-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+12}-4=3x-6+\sqrt{x^2+5}-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^2-4}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}=3\left(x-2\right)+\frac{x^2-4}{\sqrt{x^2+5}+3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}-\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+5}+3}-3\right)=0\)
Vì \(\sqrt{x^2+12}+4>\sqrt{x^2+5}+3\Rightarrow\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}< \frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+5}+3}\)
Do đó : \(\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+12}+4}-\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+5}+3}-3< 0\)nên x - 2 = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\)x = 2
Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên x^ 2 +x +1 = 2xy +y
pt <=> x^2+x+1-(2xy+y) = 0
<=> (x^2+1/2.x)+(1/2.x+1/4)-y.(2x+1)+3/4=0
<=> 1/2.x.(2x+1)+1/4.(2x+1)-y.(2x+1) = -3/4
<=> (2x+1).(1/2.x+1/4-y) = -3/4
<=> (2x+1).(2x+1-4y) = -3
Đến đó bạn tự giải nha ( dùng ước bội )
Tk mk nha
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
giải phương trình:
\(x^3-x^2-x-2=0\)
\(\frac{x^2}{\sqrt{3x-2}}-\sqrt{3x-2}=1-x\)
tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình;
\(2x^2+y^2-2xy+2y-6x+5=0\)
Bài 1 :
a) \(x^3-x^2-x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-2x^2+x^2-2x+x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-2x^2\right)+\left(x^2-2x\right)+\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-2\right)+x\left(x-2\right)+\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)(1)
Vì \(x^2+x+1=x^2+2.\frac{1}{2}.x+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\)
Vì \(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)\(\Rightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ge\frac{3}{4}\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+x+1\ge\frac{3}{4}\forall x\)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) \(\Rightarrow x-2=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(x=2\)
Bài 2:
\(2x^2+y^2-2xy+2y-6x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2xy+y^2-2x+2y+1+x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)-\left(2x-2y\right)+1+\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)^2-2\left(x-y\right)+1+\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y-1\right)^2+\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)(1)
Vì \(\left(x-y-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\); \(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-y-1\right)^2+\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) \(\Rightarrow\left(x-y-1\right)^2+\left(x-y\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-y-1=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}y=x-1\\x=2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}y=1\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x=2\)và \(y=1\)
Bài 1 : tìm x ; y nguyên dương
2xy + x + y = 83
Bài 2 tìm nghiệm nguyên của phương trình :
a ) x2 + 2y2 + 3xy - x - y + 3 = 0
b ) 6x2y3 + 3x2 - 10y3 = -2























