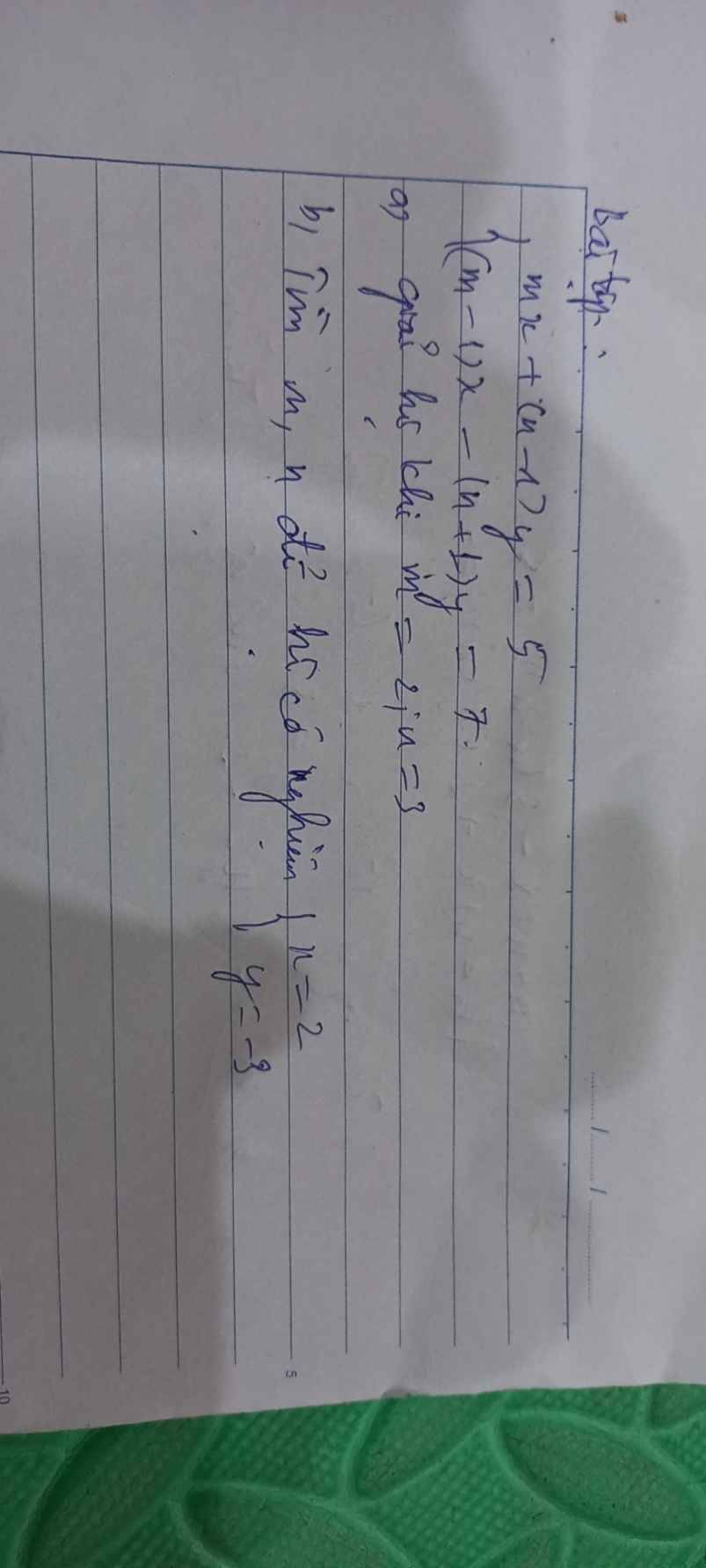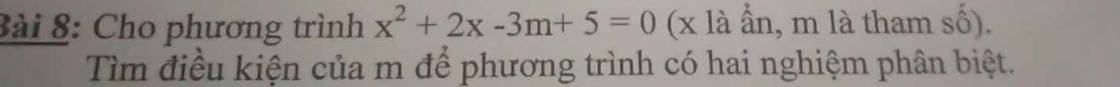 help mik với:S
help mik với:S
Bài 3: Giải hệ phương trình bằng phương pháp thế
\(\Delta=2^2-4.1\left(-3m+5\right)\)= 4+12m-20 = 12m-16
Để pt có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\Delta>0\)
<=>12m -16>0
<=>12m>16
=>\(m>\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
a: Thay m=2 và n=3 vào hệ phương trình, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+\left(3-1\right)y=5\\\left(2-1\right)x-\left(3+1\right)y=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2y=5\\x-4y=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2y=5\\2x-8y=14\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}10y=-9\\x-4y=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{9}{10}\\x=4y+7=4\cdot\dfrac{-9}{10}+7=\dfrac{-36+70}{10}=\dfrac{34}{10}=\dfrac{17}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Thay x=2 và y=-3 vào hệ phương trình, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m+\left(n-1\right)\cdot\left(-3\right)=5\\2\left(m-1\right)-\left(n+1\right)\cdot\left(-3\right)=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m-3n+3=5\\2m-2+3n-3=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m-3n=2\\2m+3n=7+2+3=12\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4m=14\\2m-3n=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{7}{2}\\3n=2m+2=2\cdot\dfrac{7}{2}+2=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{7}{2}\\n=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (1)
Mình dg cần rất gấp luon ạ mog mn giúp đỡ
Bài 5:
Thay x=1 và y=2 vào hệ phương trình, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-m\cdot1+2=-2m\\1+m^2\cdot2=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2m=-m+2\\2m^2=8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2=4\\-m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m=-2
Bài 6:
a: ĐKXĐ: x>=1 và y>=-2
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-1}-3\sqrt{y+2}=2\\2\sqrt{x-1}+5\sqrt{y+2}=15\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sqrt{x-1}-6\sqrt{y+2}=4\\2\sqrt{x-1}+5\sqrt{y+2}=15\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-11\sqrt{y+2}=-11\\\sqrt{x-1}-3\sqrt{y+2}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{y+2}=1\\\sqrt{x-1}=2+3=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y+2=1\\x-1=25\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=26\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\left(nhận\right)\)
b: ĐKXĐ: x<>0 và y<>0
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{12}\\\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{15}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{8}{y}=\dfrac{8}{12}=\dfrac{2}{3}\\\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{15}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{7}{y}=\dfrac{-1}{3}\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=21\\\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{21}=\dfrac{7-4}{84}=\dfrac{3}{84}=\dfrac{1}{28}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=28\\y=21\end{matrix}\right.\left(nhận\right)\)
c: ĐKXĐ: x<>0 và y<>2
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y-2}=4\\\dfrac{4}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y-2}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{4}{x}+\dfrac{6}{y-2}=8\\\dfrac{4}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y-2}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7}{y-2}=7\\\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y-2}=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y-2=1\\\dfrac{2}{x}=4-\dfrac{3}{1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\left(nhận\right)\)
d: ĐKXĐ: x<>-2y và x<>-y/2
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x+2y}+\dfrac{1}{2x+y}=3\\\dfrac{4}{x+2y}-\dfrac{3}{2x+y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{6}{x+2y}+\dfrac{3}{2x+y}=9\\\dfrac{4}{x+2y}-\dfrac{3}{2x+y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{10}{x+2y}=10\\\dfrac{4}{x+2y}-\dfrac{3}{2x+y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=1\\\dfrac{3}{2x+y}=4-1=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=1\\2x+y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y=2\\2x+y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3y=1\\x+2y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=1-\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\left(nhận\right)\)
e: ĐKXĐ: x>4 và y<>-2
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x-4}}+\dfrac{4}{y+2}=7\\\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x-4}}-\dfrac{1}{y+2}=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x-4}}+\dfrac{4}{y+2}=7\\\dfrac{20}{\sqrt{x-4}}-\dfrac{4}{y+2}=16\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{23}{\sqrt{x-4}}=23\\\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x-4}}-\dfrac{1}{y+2}=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-4}=1\\\dfrac{1}{y+2}=5-4=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-4=1\\y+2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\left(nhận\right)\)
f: ĐKXĐ: x>=-1
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x+y\right)+\sqrt{x+1}=4\\\left(x+y\right)-\sqrt{x+1}=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x+y\right)+\sqrt{x+1}+\left(x+y\right)-\sqrt{x+1}=4-5=-1\\\left(x+y\right)-\sqrt{x+1}=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\left(x+y\right)=-1\\\sqrt{x+1}=-\dfrac{1}{3}+5=\dfrac{14}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x+1=\dfrac{196}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{187}{9}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{187}{9}=-\dfrac{190}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\left(nhận\right)\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Nhiều quá em, em chỉ nên đăng những câu nào cảm thấy khó khăn khi giải quyết thôi
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Xuôi 80km ; ngược 80km hết 9h ; Vcan = 18km/h . Tìm Vnứớc
Cho hệ phương trình\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-my=4\\-2x+2y=4m\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) Vô nghiệm
b) Có 1 nghiệm duy nhất
c) Có vô số nghiệm
a: Để hệ phương trình vô nghiệm thì
\(\dfrac{1}{-2}=\dfrac{-m}{2}< >\dfrac{4}{4m}=\dfrac{1}{m}\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{m}{2}\\-m^2< >2\left(luônđúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=1\)
b: Để hệ phương trình có 1 nghiệm duy nhất thì \(\dfrac{1}{-2}< >\dfrac{-m}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{2}\ne\dfrac{m}{2}\)
=>\(m\ne1\)
c: Để hệ có vô số nghiệm thì \(\dfrac{1}{-2}=\dfrac{-m}{2}=\dfrac{4}{4m}\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{m}{2}\\\dfrac{-m}{2}=\dfrac{1}{m}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m^2=-2\left(vôlý\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Giải hệ phương trình bằng phương pháp thế\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4\left(x+y\right)+y=6\\3\left(x+y\right)+y=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>4x+4y+y=6 và 3x+3y+y=8
=>4x+5y=6 và 3x+4y=8
=>12x+15y=18 và 12x+16y=32
=>-y=-14 và 4x+5y=6
=>y=14 và 4x=6-5y=6-70=-64
=>x=-16 và y=14
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) 2x-3y=1
-x+4y=7
b) x+3y=7
2x-3y=8
a: 2x-3y=1 và -x+4y=7
=>2x-3y=1 và -2x+8y=14
=>5y=15 và 2x-3y=1
=>y=3 và 2x=1+3y=10
=>x=5 và y=3
b; x+3y=7 và 2x-3y=8
=>3x=15 và 2x-3y=8
=>x=5 và 3y=2x-8=2*5-8=10-8=2
=>x=5 và y=2/3
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
a) x+y=5
2x-y=1
b) 5x+2y=4
x-2y=8
\(a)\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=5\\2x-y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=5-x\\2x-\left(5-x\right)=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=5-x\\3x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=5-x\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=5-2\\x=2\end{matrix}\right. \\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b)\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x+2y=4\\x-2y=8\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5\left(8+2y\right)+2y=4\\x=8+2y\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}40+10y+2y=4\\x=8+2y\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}12y=-36\\x=8+2y\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\x=8+2.\left(-3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 7
Bình luận (1)
THAM KHẢO NHÉ: {2x−y=55x+2y=8{2�−�=55�+2�=8 Hãy tìm nghiệm của y� {y=2x−55x+2y=8{�=2�−55�+2�=8 Hãy thay thế giá trị y� đã cho vào phương trình 5x+2y=85�+2�=85x+2(2x−5)=85�+2(2�−5)=8 Hãy tìm nghiệm của x�
{y=2x−55x+2y=8{�=2�−55�+2�=8 Hãy thay thế giá trị y� đã cho vào phương trình 5x+2y=85�+2�=85x+2(2x−5)=85�+2(2�−5)=8 Hãy tìm nghiệm của x� x=2�=2 Hãy thay thế giá trị x� đã cho vào phương trình y=2x−5�=2�−5y=2×2−5�=2×2−5 Hãy sắp xếp biểu thức
x=2�=2 Hãy thay thế giá trị x� đã cho vào phương trình y=2x−5�=2�−5y=2×2−5�=2×2−5 Hãy sắp xếp biểu thức  y=−1�=−1 Nghiệm có khả năng như sau x=2,y=−1�=2,�=−1 Hãy kiểm tra xem có phải là nghiệm của hệ phương trình không {2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8{2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8 Hãy đơn giản hóa đẳng thức
y=−1�=−1 Nghiệm có khả năng như sau x=2,y=−1�=2,�=−1 Hãy kiểm tra xem có phải là nghiệm của hệ phương trình không {2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8{2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8 Hãy đơn giản hóa đẳng thức  {5=58=8{5=58=8 Vì nó đúng với cả hai phương trình nên nó là nghiệm của hệ phương trình x=2,y=−1
{5=58=8{5=58=8 Vì nó đúng với cả hai phương trình nên nó là nghiệm của hệ phương trình x=2,y=−1
 {y=2x−55x+2y=8{�=2�−55�+2�=8 Hãy thay thế giá trị y� đã cho vào phương trình 5x+2y=85�+2�=85x+2(2x−5)=85�+2(2�−5)=8 Hãy tìm nghiệm của x�
{y=2x−55x+2y=8{�=2�−55�+2�=8 Hãy thay thế giá trị y� đã cho vào phương trình 5x+2y=85�+2�=85x+2(2x−5)=85�+2(2�−5)=8 Hãy tìm nghiệm của x� x=2�=2 Hãy thay thế giá trị x� đã cho vào phương trình y=2x−5�=2�−5y=2×2−5�=2×2−5 Hãy sắp xếp biểu thức
x=2�=2 Hãy thay thế giá trị x� đã cho vào phương trình y=2x−5�=2�−5y=2×2−5�=2×2−5 Hãy sắp xếp biểu thức  y=−1�=−1 Nghiệm có khả năng như sau x=2,y=−1�=2,�=−1 Hãy kiểm tra xem có phải là nghiệm của hệ phương trình không {2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8{2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8 Hãy đơn giản hóa đẳng thức
y=−1�=−1 Nghiệm có khả năng như sau x=2,y=−1�=2,�=−1 Hãy kiểm tra xem có phải là nghiệm của hệ phương trình không {2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8{2×2−(−1)=55×2+2×(−1)=8 Hãy đơn giản hóa đẳng thức  {5=58=8{5=58=8 Vì nó đúng với cả hai phương trình nên nó là nghiệm của hệ phương trình x=2,y=−1
{5=58=8{5=58=8 Vì nó đúng với cả hai phương trình nên nó là nghiệm của hệ phương trình x=2,y=−1
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
a) x-y=-5
2x+y=11
b) x+4y=11
5x-7y=1
a: x-y=-5 và 2x+y=11
=>x-y+2x+y=11-5=6 và x-y=-5
=>3x=6 và x-y=-5
=>x=2 và y=2-(-5)=7
b; x+4y=11 và 5x-7y=1
=>5x+20y=55 và 5x-7y=1
=>27y=54 và x+4y=11
=>y=2 và x=11-8=3
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
a) 3x+y=1
x-2y=5
b) 2x+y=8
-x+y=2
\(a,\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+y=1\\x-2y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-3x\\x-2.\left(1-3x\right)=5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-3x\\x-2+6x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-3x\\7x=7\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=8\\-x+y=2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=8-2x\\-x+8-2x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=8-2x\\-3x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=8-2.2\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=4\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)